Notably, the Dragonfly launch was one of the first times United Launch Alliance has been eligible to bid its new Vulcan rocket for a NASA launch contract. NASA officials gave the green light for the Vulcan rocket to compete head-to-head with SpaceX’s Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy after ULA’s new launcher had a successful debut launch earlier this year. With this competition, SpaceX came out on top.
A half-life of 88 years
NASA’s policy for new space missions is to use solar power whenever possible. For example, Europa Clipper was originally supposed to use a nuclear power generator, but engineers devised a way for the spacecraft to use expansive solar panels to capture enough sunlight to produce electricity, even at Jupiter’s vast distance from the Sun.
But there are some missions where this isn’t feasible. One of these is Dragonfly, which will soar through the soupy nitrogen-methane atmosphere of Titan. Saturn’s largest moon is shrouded in cloud cover, and Titan is nearly 10 times farther from the Sun than Earth, so its surface is comparatively dim.
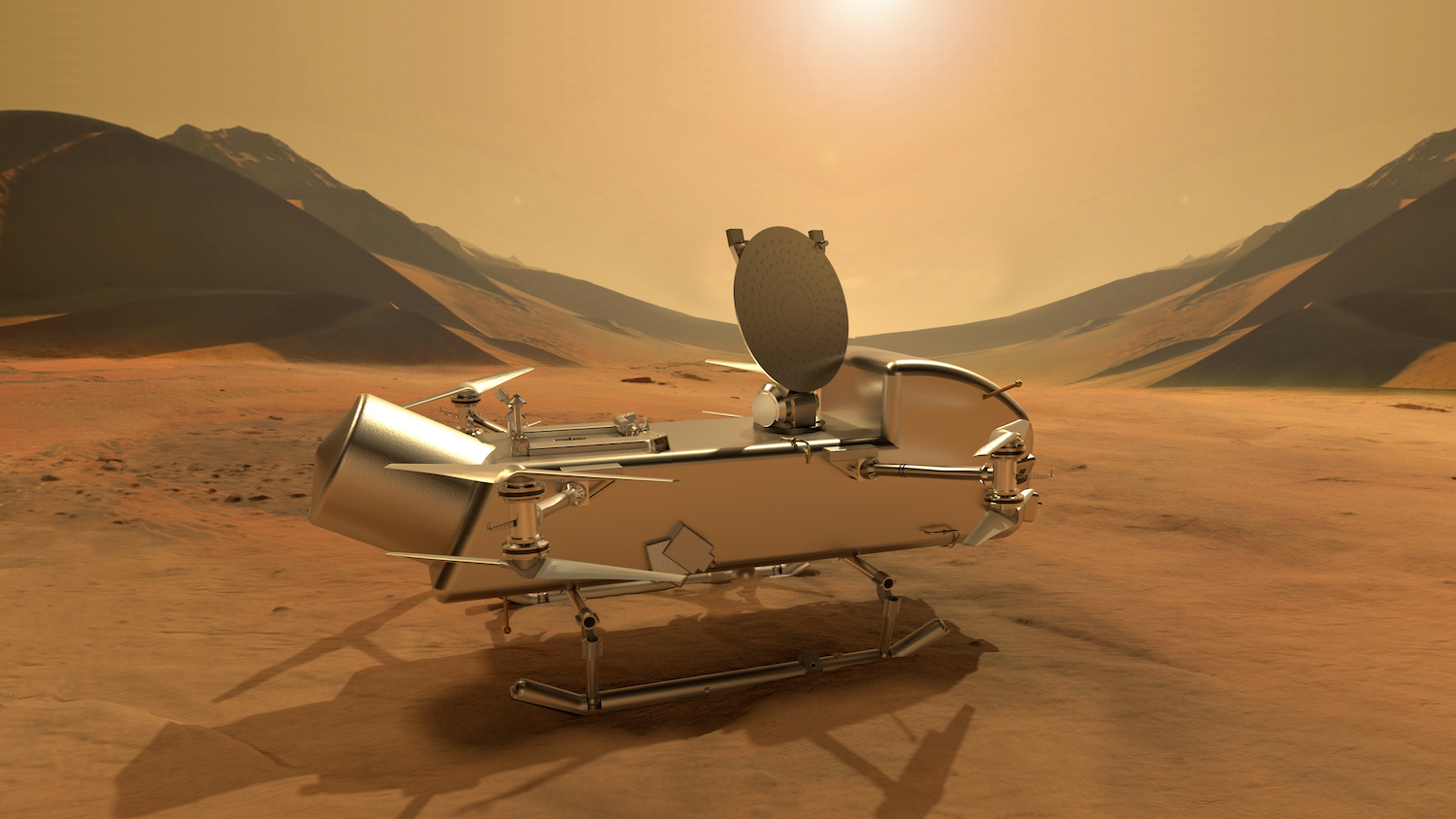
Credit:
NASA/JHUAPL/Steve Gribben
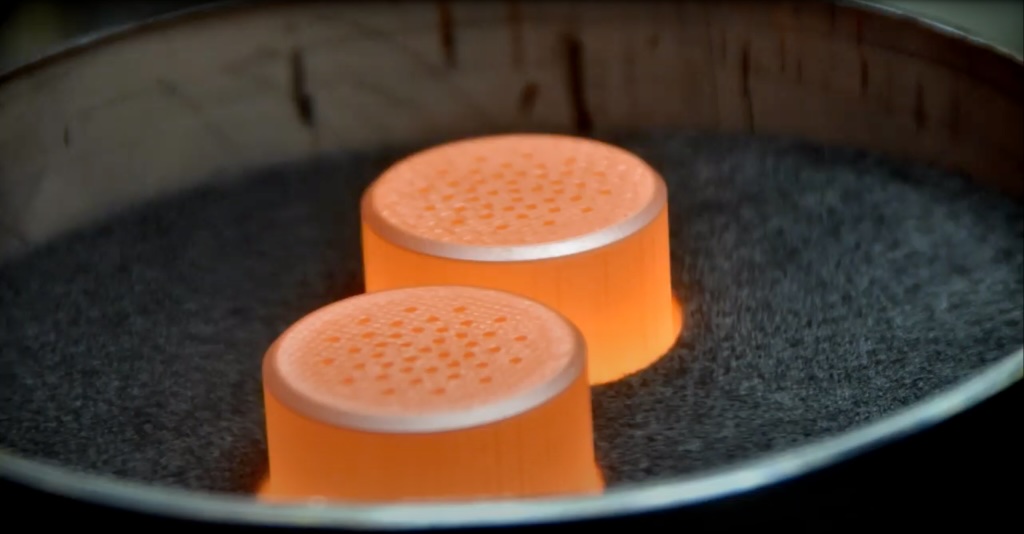
Dragonfly will launch with about 10.6 pounds (4.8 kilograms) of plutonium-238 to fuel its power generator. Plutonium-238 has a half-life of 88 years. With no moving parts, RTGs have proven quite reliable, powering spacecraft for many decades. NASA’s twin Voyager probes are approaching 50 years since launch.
The Dragonfly rotorcraft will launch cocooned inside a transit module and entry capsule, then descend under parachute through Titan’s atmosphere, which is four times denser than Earth’s. Finally, Dragonfly will detach from its descent module and activate its eight rotors to reach a safe landing.
Once on Titan, Dragonfly is designed to hop from place to place on numerous flights, exploring environments rich in organic molecules, the building blocks of life. This is one of NASA’s most exciting, and daring, robotic missions of all time.
After launching from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in July 2028, it will take Dragonfly about six years to reach Titan. When NASA selected the Dragonfly mission to begin development in 2019, the agency hoped to launch the mission in 2026. NASA later directed Dragonfly managers to target a launch in 2027, and then 2028, requiring the mission to change from a medium-lift to a heavy-lift rocket.
Dragonfly has also faced rising costs NASA blames on the COVID-19 pandemic and supply chain issues and an in-depth redesign since the mission’s selection in 2019. Collectively, these issues caused Dragonfly’s total budget to grow to $3.35 billion, more than double its initial projected cost.

